The New CompTIA PenTest+ V3 Review: How I Passed My First Hacking Cert
My CompTIA PenTest+ Journey (v2 → v3): What I Learned, What Surprised Me, and a practical Nmap cheatsheet for aspiring pentesters.
☕ Before You Start Reading…
This is a long post. Not a “5-minute skim while scrolling” kind of post.
So before we begin, I highly recommend you:
- ☕ Grab a coffee, tea, or your favorite drink
- 🪑 Sit somewhere comfortable
Alright, now we’re ready 😄
In this post, I’ll share why I took the CompTIA PenTest+ exam, how I navigated the v2 → v3 transition, what actually surprised me during the exam, common mistakes new candidates make, and finally a practical Nmap cheatsheet you can use for your own preparation.
ℹ️ Introduction
CompTIA PenTest+ is a vendor-neutral penetration testing certification designed to validate the theoretical knowledge and professional practices required for real-world penetration testing engagements.
It covers areas such as planning and scoping, legal and compliance requirements, reconnaissance, vulnerability analysis, social engineering, and reporting, making it a strong foundation for anyone looking to start or formalize a career in penetration testing.
Official details such as exam objectives, pricing, recommended experience, and current exam versions are maintained by CompTIA and should always be reviewed before beginning preparation. 🔗 CompTIA PenTest+ Certification V3 (New Version)  CompTIA PenTest+ v3 Certification
CompTIA PenTest+ v3 Certification
🚀 My CompTIA PenTest+ Journey (v2 → v3)
I took the CompTIA PenTest+ exam after I won a full exam bundle during a recent penetration testing competition.
Winning the voucher felt like a no-brainer opportunity, until I realized something important:
- The study material I received was for PenTest+ version 2
- My actual exam was PenTest+ version 3
So yes… I had to bridge the gap myself.
This meant:
- Comparing v2 and v3 objectives
- Identifying new and expanded topics
- Updating my notes with real-world pentesting techniques
It wasn’t just “study the book and pass.”. It required extra effort, research, and validation.
⚖️ Why PenTest+ Matters Before the Career Starts
This is something I want to be very clear about:
CompTIA PenTest+ provides the theoretical foundation every penetration tester should have before diving deep into technical exploitation.
Before you:
- Spam Metasploit modules
- Jump into red teaming
- Or chase advanced exploit development
You need to understand:
- Scope and authorization
- Legal boundaries
- Risk management
- Pentesting methodologies and frameworks
- Professional reporting and decision-making
PenTest+ teaches you how to think like a professional penetration tester, not just how to “hack things.”
To be honest, that foundation matters a lot.
🧠 Exam Difficulty & The Right Mindset
PenTest+ is not an entry-level exam, regardless of how it’s sometimes marketed.
You need to approach it with the mindset of:
- A junior-to-mid penetration tester
- Someone who understands why an action is taken
- A professional who respects rules of engagement and impact
During the exam, I constantly reminded myself:
- Think like a consultant
- Choose the least risky, most professional option
- Read every scenario as if it’s a real engagement
This mindset helps more than memorizing tools.
😲 What Surprised Me (The PBQ Factor)
What surprised me the most was the difficulty of some Performance-Based Questions (PBQs).
I encountered:
- Advanced pentesting commands
- Output that required real interpretation, not guessing
- Scenarios where multiple tools could work, but only one made sense
These PBQs weren’t testing:
“Do you know this command?”
They were testing:
“Do you understand what this output means, and what to do next?”
If you’ve never:
- Analyzed Nmap results
- Used Burp Suite meaningfully
- Followed scan → exploit → report workflows
…these questions can feel brutal.
❌ Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are mistakes I see very often:
⚠️ Focusing Only on Tools
PenTest+ is more about process and reasoning than tool memorization.
⚠️ Ignoring Laws and Scope
Legal authorization, compliance, and scope violations are exam favorites.
⚠️ Underestimating Social Engineering
Human attacks are heavily tested and often underestimated.
📌 CompTIA PenTest+ Cheatsheet (Quick Review)
Below is a condensed cheat sheet I built because I can’t share all my notes here, but here is an example of how I personally organized my notes:  Organized Notes
Organized Notes
1. Engagement management (13%)
1.1 Legal & Compliance Framework
Contract Types Matrix
| Contract Type | Purpose | Key Contents | Exam Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSA (Master Service Agreement) | Overall business relationship | High-level scope, invoicing, liability limits, insurance | Relationship governance |
| SOW (Statement of Work) | Specific engagement details | In/out scope, timelines, deliverables, payment milestones | Scope definition |
| ToS (Terms of Service) | Tester behavior rules | Penalties for scope violations, data misuse | Legal protection |
| SLA (Service Level Agreement) | Service quality metrics | Uptime guarantees, response times, termination clauses | Performance standards |
Compliance & Privacy Cheat Sheet
| Framework / Law | Key Focus | Applicability / Use Case | Notes / Exam Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCI DSS | Secure systems, strong access control, continuous monitoring | Companies handling credit card data | Compliance lifecycle: Assess → Remediate → Report; Merchant levels 1–4; Failing = fines or losing card processing |
| GDPR | Explicit consent, minimal data collection | EU residents’ personal data (applies globally) | Users can withdraw consent; 72‑hour breach notification |
| HIPAA | Healthcare data protection | US healthcare sector | Ensures patient privacy & security of health info |
| CCPA | California privacy law | Personal data of California residents | GDPR-like rules; consumer rights focus |
| SOX | Financial reporting accuracy | Corporate financial data | Ensures accountability & legal compliance |
| FISMA / CMMC | Government & defense system security | US federal agencies & contractors | Security & compliance standards |
| ISO 27001 / 27002 | Information security management framework | Organizations’ security programs | Provides structured security policies & best practices |
Authorization Requirements
- Who: Authorized testers (certifications verified)
- What: Exact IP ranges, domains, apps, cloud resources
- When: Validity period, testing windows
- Data handling: Encryption, disposal, NDAs
- Stop conditions: Emergency contacts, incident procedures
1.2 Scope Definition Elements
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
**INCLUDE in scope:
├── Networks: CIDR ranges, ASNs, wired/wireless
├── Applications: Web (sites/pages/roles), Mobile (platforms/versions), APIs
├── Cloud: SaaS/IaaS/PaaS (provider permissions required)
├── Physical: Onsite locations, server rooms
└── Social: Specific user targets`
**EXCLUDE explicitly:
├── Production systems (prefer sandbox)
├── Third-party dependencies (need separate auth)
├── Fragile legacy/IoT systems
1.3 Assessment Strategies
Testing Methodologies Overview
| Type | Knowledge | Use Case | Pros / Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black Box | Zero information | Real attacker simulation | Realistic / Time-intensive |
| Grey Box | Limited credentials | Web application testing | Focused / Less comprehensive |
| White Box | Full access | Code review, deep testing | Thorough / Less realistic |
1.4 Threat Modeling Frameworks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
**STRIDE** (Web/Application):
- S : Spoofing (auth bypass)
- T : Tampering (data integrity)
- R : Repudiation (no logging)
- I : Information Disclosure
- D : Denial of Service
- E : Elevation of Privilege
**DREAD** (Risk Scoring):
- D : Damage potential
- R : Reproducibility
- E : Exploitability
- A : Affected users
- D : Discoverability
Standards & Frameworks:
| Framework | Focus | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| OWASP | Web apps | Application security |
| NIST SP 800-115 | General | Structured testing |
| OSSTMM | Metrics-driven | Comprehensive audits (Holistic) |
| PTES | Full lifecycle | Complete pentests |
| MITRE ATT&CK | TTPs | Real-world attacks |
| ISSAF | Open-source | End-to-end guidance |
2.RECONNAISSANCE & ENUMERATION (21%)
2.1 Passive OSINT Collection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
**Social Media (LinkedIn/FB/X/IG):
- Employee roles/hierarchy
- PII for social engineering
- Company culture insights
**Job Boards (Indeed/Glassdoor):
- Tech stack (AWS, Python, Splunk)
- Staffing gaps (under-resourced teams)
- Software architecture hints
Google Dorking
Useful operators: site: - filetype: - intitle: - inurl:
Used to find: Exposed documents - Login portals - Backup files
2.2 DNS Enumeration Arsenal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
**Record Types & Commands:
A → nslookup target.com
MX → dig mx target.com
NS → dig ns target.com
TXT → dig txt target.com
SRV → dig srv _service._proto.domain
**Enumeration Techniques:
1. Zone Transfer: `dig @ns1.target.com target.com AXFR`
2. Subdomain Bruteforce: `subfinder -d target.com`
3. Reverse DNS: `nslookup 192.168.1.1`
DNS Tools
| Tool | Capabilities | Commands |
|---|---|---|
| nslookup | Interactive/non-interactive | nslookup target 8.8.8.8set type=MX |
| dig | Advanced queries | dig ns target.comdig axfr @ns.target.com domain |
| DNSDumpster | Visual subdomain maps | Web GUI |
| Amass | Automated enum | amass enum -d target.com |
| theHarvester | Emails/subdomains | theHarvester -d target -b all |
2.3 User Enumeration Methods
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
**Techniques:
SSH Banner: ssh target.com (misconfig reveals users)
SNMP: snmpwalk -v2c -c public target .1.3.6.1.4.1.77.1.2.25
SMTP: Metasploit auxiliary/scanner/smtp/smtp_enum
**Tools:
├── theHarvester: Email harvesting
├── Hunter.io: Corporate emails
├── Sherlock: Username across platforms
└── Social-Searcher: Real-time mentions
3. ATTACKS & EXPLOITS (35%)
3.1 Network Scanning Mastery
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
**Host Discovery:
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24 # Ping sweep
nmap -Pn 192.168.1.0/24 # Skip discovery
nmap --script discovery 192.168.1.1
**Stealth Techniques:
-D RND:3 # Random decoys
-f # Fragment packets (8-byte)
--spoof-mac 0 # Random MAC for spoofing
--source-port 53 # DNS port bypass (spoofing)
-sF # FIN scan (bypass stateless FW)
Scan Types Comparison:
| Scan | Flags | Stealth | Firewall Bypass |
|---|---|---|---|
| SYN | -sS | High | Most firewalls |
| FIN | -sF | Very High | Stateless FW |
| NULL | -sN | Very High | Stateless FW |
| XMAS | -sX | Very High | Stateless FW |
3.2 Vulnerability Scanning
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
**Considerations:
✅ Bandwidth consumption
✅ Fragile systems (IoT/legacy)
✅ Query throttling
✅ Production vs non-prod
**Scanner Pipeline:
nmap -p80,443 10.0.1.0/24 -oG - | nikto.pl -h -
Scanners Tools
| Tool | Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVAS | Open-source | Comprehensive | Resource heavy |
| Nessus | Commercial | Accurate | Expensive |
| Nexpose | Commercial | Risk scoring | Complex |
| Nikto | Web | Fast web scans | Limited scope |
| Burp | Web proxy | Manual testing | Learning curve |
3.3 Web Application Attacks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
**OWASP Top 10 Coverage:
├── Injection (SQLi, Command): sqlmap, Burp Intruder
├── XSS: Burp Repeater, manual payloads
├── RFI/LFI: ../../etc/passwd
├── Session: Hijacking/Fixation
├── CSRF
└── SSRF
Burp Suite Workflow:
- Proxy → Intercept requests
- Target → Site map
- Repeater → Manual testing
- Intruder → Payload attacks
- Collaborator → OOB detection
3.4 Specialized Attack Vectors
| Vector | Tools | Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Wireless | Aircrack-ng, WGLE | WEP/WPA2 |
| Cloud | Pacu, Prowler, ScoutSuite | AWS/Azure misconfigs |
| Mobile | MobSF, Frida, Drozer | APK analysis |
| Physical | Lockpicks, USB Rubber Ducky | Tailgating, bypass |
Social Engineering Variants:
Phishing ← Spear ← Whaling (C-Level)
Vishing (VoIP) - SPIT (auto VoIP)
SMiShing (SMS) - Spim (IM spam)
4. VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS (17%)
4.1 Attack Surface Mapping
1
2
3
4
**Discovery Tools:
Censys/Shodan → Exposed ports/services
Zenmap → Topology visualization
ARP/SNMP/WMI → Internal mapping
Prioritization Framework:
CVSS → Severity score (0-10)
CVE → Specific vulnerability ID
CWE → Weakness category
DREAD → Business risk
4.2 Validation Process
- Automated scan → Identify candidates
- Manual verification → Reduce false positives
- Metasploit → Exploit validation
- Burp/Repeater → Web app confirmation
5. Post-exploitation and lateral movement (14%)
5.1 Post-Exploitation Techniques
Persistence:
1
2
3
4
5
6
├── Backdoors (Meterpreter)
├── Scheduled tasks/cron
├── Registry run keys
├── SSH keys
Lateral Movement:
1
2
3
4
├── Pass-the-Hash
├── Pivot (Meterpreter)
├── RDP/WinRM
└── CrackMapExec
5.2 Covering Tracks
Mandatory Cleanup:
1
2
3
4
5
❌ Remove shells
❌ Delete created credentials
❌ Clear logs (carefully)
❌ Remove tools
✅ Document everything first
5.3 Reporting Structure
Executive Summary:
1
2
3
├── Risk rating
├── Business impact
├── Top 3 findings
Technical Details:
1
2
3
4
├── Screenshots
├── Commands used
├── CVSS scores
├── Proof-of-concept
Remediation:
1
2
3
├── Technical controls
├── Administrative controls
└── Physical controls
COMMAND CHEATSHEET
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Recon
theHarvester -d target -b all
dig axfr @ns.target.com domain
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24
# Stealth Scanning
nmap -sS -sV --randomize-hosts -D RND:3 target
nmap -f --source-port 53 target
# Web Pipeline
nmap -p80,443 10.0.0.0/24 -oG - | nikto.pl -h
# DNS Enum
nslookup target 8.8.8.8
dig ns target.com
🔍 The Ultimate Nmap Cheatsheet (Exam Favorite)
Before you start reading, if you want a Github version check this link Github Version
Nmap Enumeration
FAST command :
sudo nmap -A -F -T4 --script=vuln <IP> -F to scan the top 100 ports -p- to scan all the ports
Target Specification
nmap 192.168.1.1→ Scan a single IPnmap 192.168.1.1-254→ Scan a rangenmap [scanme.nmap.org](http://scanme.nmap.org/)→ Scan a domainnmap 192.168.1.0/24→ CIDR scannmap -iL targets.txt→ Scan from file
Host Discovery
-sL→ List targets only-snOR-sP(in old version)→ Disable port scanning-Pn→ Port scan only (disable host discovery)-PR→ ARP discovery on local network (ARP ping)-n→ No DNS resolution
Scan Techniques
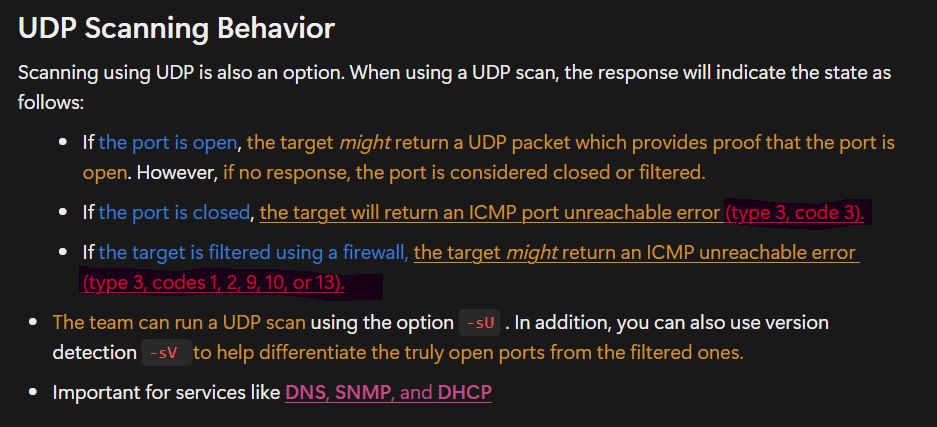
-sS→ TCP SYN scan (default) it also called as SYN Stealth scan-sT→ Full TCP connect scan-sU→ UDP port scan-sA→ TCP ACK scan-sX→ Christmas tree scan (TCP segment with the FIN, PSH, and URG flags raised to bypass a firewall or IDS)-sW→ TCP Window scan- if a firewall is blocking the default ICMP pings, the team has other options. For example, they can try the following check this page :
- TCP ACK Ping
-PA <portlist>This will set the acknowledgement (ACK) flag in the TCP header. - UDP Ping
-PU <portlist>This scan uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP). - SCTP Initiation Ping
-sY <portlist>This scan uses the Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) , an alternative to using either a TCP or UDP scan to see if a host is alive. - TCP SYN Ping
-PS <target>This sends an empty TCP packet with the SYN flag set to whatever port(s) you specify. If you don’t indicate a port number, Nmap will try all ports and then display the findings.
- TCP ACK Ping
Port Specification
-p 21→ Specific port-p 21-100→ Port range-p-→ All ports-F→ Fast scan (100 ports)--top-ports 2000→ Top port
| Port State | Description |
|---|---|
| OPEN | The port is open and responding to probes. |
| CLOSED | The port is not responding to probes. |
| FILTERED | The port is blocked by a firewall. |
| UNFILTERED | The port is accessible; however, Nmap is unable to determine if the port is open or closed. |
Service & Version Detection
-sV→ Detect service versions--version-intensity <0-9>→ Adjust accuracy/speed--version-light→ Faster, less accurate--version-all→ Full intensity-A→ OS, version, scripts, tracerout
- Example 1: Using Netcat for Banner Grabbing:
nc -v <target.com> <80>HEAD / HTTP/1.1
- Example 2 : Metasploit Auxiliary Module:
use auxiliary/scanner/http/http_versionset RHOSTS target.comrun
OS Detection
-O→ OS detection--osscan-limit→ Requires open & closed ports--osscan-guess→ Aggressive guessing-A→ OS + version + scripts + traceroute
Timing & Performance
-T0→ Paranoid (IDS evasion)-T3→ Normal (default)-T4→ Aggressive (fast networks)-T5→ Insane (very fast networks)--min-rate <num>→ Minimum packet rate--max-rate <num>→ Maximum packet rate
Firewall / IDS Evasion
-f→ Fragment packets-D <decoys>→ Decoy scans-S <IP>→ Spoof source IP--proxies <proxylist>→ Use proxies--data-length <num>→ Append random data
| Stealth Option | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
-sF | nmap -sF www.company.tld | This option sends a TCP FIN to bypass a non-stateful firewall. |
-f | nmap -f 192.168.1.50 | This will split the packets into 8-byte fragments to make it harder for packet filtering firewalls and intrusion detection to identify the true purpose of the packets. |
--randomize-hosts | nmap --randomize-hosts 192.168.1.1-100 | This option will randomize the order of the hosts being scanned. |
NSE Scripts
-sC→ Default safe scripts--script <name>→ Run specific script--script http*.→ Run script category--script-args <args>→ Pass arguments- Examples:
http-sitemap-generator, smb-enum*, dns-brute
Output Options
-oN <file>→ Normal output-oX <file>→ XML output-oG <file>→ Grepable output-oS <file>→ script output-oA <prefix>→ All formats-v/-vv→ Verbosity levels
Ports and Services
| Feature | Port 111 | Port 135 |
|---|---|---|
| OS | Unix/Linux | Windows |
| RPC Type | ONC RPC (SunRPC) | DCE/RPC (MSRPC) |
| Service | Portmapper / rpcbind | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| Main Uses | NFS, NIS, mountd | DCOM, AD, WMI, Windows services |
| Assigns Ports For | Unix RPC services | Windows RPC services |
| Port | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 21/20 | FTP | File transfer (control channel) |
| 23 | Telnet | |
| 25 | SMTP | Email sending between mail servers |
| 389 | LDAP | Active Directory is probably running. |
| 1433 | SQL server | SQL server listen on TCP port. |
| 1434 | SQL server | SQL server listen on UDP port. |
| 2049 | NFS | The main communication channel for sharing files and directories over a network, predominantly in Linux and Unix-like environments. |
| Feature | SMB | NetBIOS |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | File-sharing protocol | Communication API/protocol |
| Purpose | File & printer sharing | Name services, sessions |
| Port | 445 (or 139 via NetBIOS) | 137, 138, 139 |
| Dependency | No longer needs NetBIOS | Does not provide file sharing |
route add <destination> mask <netmask> <gateway> The route add command is used to manually add a new entry to a computer’s routing table. A routing table tells the operating system where to send network packets, especially when there are multiple networks, gateways, or interfaces.
📚 Final Advice & Study Resources
My Honest Advice
- Do hands-on practice (even basic labs help)
- Understand why you use a tool
- Treat every question like a real engagement
- Memorize laws, frameworks, and scope rules
- Stay calm — logic beats speed in PBQs
Helpful Resources
- CompTIA PenTest+ Exam Prep on Youtube
- TryHackMe Pentest+
- The Ultimate CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-002 Practice Exam 2025
- OWASP Top 10 & Testing Guide
- CompTIA PenTest+ (PT0-003) Full Course & Practice Exam
- CompTIA PenTest+ (PT0-003) 6 Practice Exams
- Your own notes (seriously writing helps retention)
🏁 Final Thoughts
PenTest+ isn’t about being the best hacker in the room.
It’s about becoming a professional penetration tester.
If you’re serious about starting or strengthening a pentesting career, this certification gives you the theoretical backbone you’ll rely on for years.
Thanks for reading, and if you made it this far, your drink is probably empty ☕😝